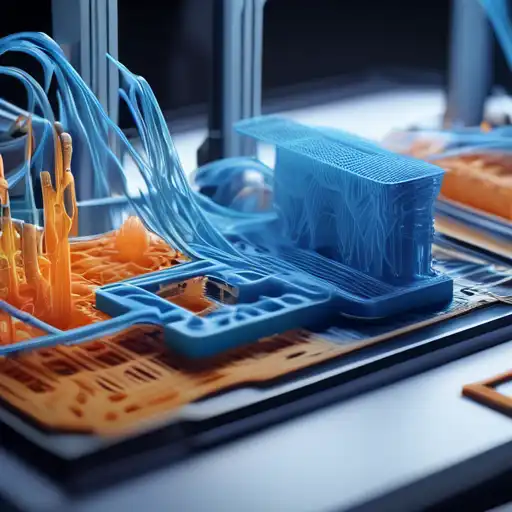
Introduction to 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This innovative technology builds objects layer by layer, offering unparalleled flexibility in design and manufacturing. From prototyping to production, 3D printing is revolutionizing industries worldwide.
The Process of 3D Printing
The journey of 3D printing begins with a digital model, typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is then sliced into thin layers by specialized software, guiding the 3D printer on how to construct the object. Materials such as plastics, metals, and even ceramics are used to bring these digital designs to life.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The most common method, where thermoplastic filaments are melted and extruded layer by layer.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): A laser sinters powdered material, bonding it together to create a solid structure.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing is not just for prototypes anymore. Its applications span across various sectors including healthcare, where it's used for creating prosthetics and bioprinting tissues; aerospace, for lightweight components; and even fashion, for customizable clothing and accessories.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing
With the ability to produce complex geometries that are impossible with traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing is setting new standards in the industry. It reduces waste, speeds up production times, and allows for mass customization.
The Future of 3D Printing
As technology advances, the potential of 3D printing continues to grow. Researchers are exploring the use of new materials, such as graphene and living cells, to expand its applications further. The future may see 3D printed buildings, organs, and even food becoming commonplace.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, 3D printing faces challenges such as high costs for industrial-grade printers, limited material options, and the need for skilled operators. However, as the technology matures, these barriers are expected to diminish.
3D printing is more than just a manufacturing technique; it's a gateway to innovation and creativity. By building objects layer by layer, it's not just creating products—it's creating the future.